How Restaurants Are Adapting to the Growing Demand for Plant-Based Meals in 2026
The restaurant industry in 2026 is rapidly evolving as consumers increasingly seek healthier, more sustainable, and ethically driven food choices. One of the most significant shifts is the rising demand for plant-based meals, which have become standard menu options across casual, fast-casual, and fine dining restaurants. Fueled by health awareness, environmental concerns, and improved plant-based ingredients, restaurants are rethinking menu design, sourcing, and kitchen operations. This article explores how plant-based dining is reshaping restaurant strategies in 2026.
What Is Driving the Growth of Plant-Based Dining in 2026
Understanding why plant-based meals have become a core part of restaurant strategies in 2026 requires examining several converging consumer, economic, and regulatory trends. The shift is not driven by a single factor but by a broader evolution in how people view food and its impact.
-
Changing Consumer Health Priorities: Consumers are more informed about nutrition and wellness, associating plant-based meals with better digestion, lower saturated fat intake, and long-term health benefits. These options appeal to flexitarians and health-conscious diners seeking variety.
-
Environmental and Climate Awareness: Plant-based food production typically requires fewer resources and generates lower emissions than animal agriculture. Restaurants that adopt sustainable menus strengthen brand trust and align with environmentally conscious customers.
-
Ethical and Cultural Shifts: Growing awareness of animal welfare, food equity, and global cuisines has normalized plant-based eating, positioning it as a responsible and inclusive choice.
-
Improved Taste and Culinary Innovation: Advances in ingredients and cooking techniques have significantly improved flavor, texture, and presentation, making plant-based dishes competitive with traditional meals.
-
Expansion Beyond Niche Audiences: Inclusive plant-based menus now appeal to mixed-diet groups, increasing satisfaction and repeat visits.
By responding to health, sustainability, ethics, and taste expectations simultaneously, restaurants in 2026 are positioning plant-based meals as a strategic growth category.
How Restaurants Are Redesigning Plant-Based Menus for Consumers
Menu development has become the primary adaptation strategy as restaurants integrate plant-based meals into their core offerings rather than treating them as add-ons or substitutions.
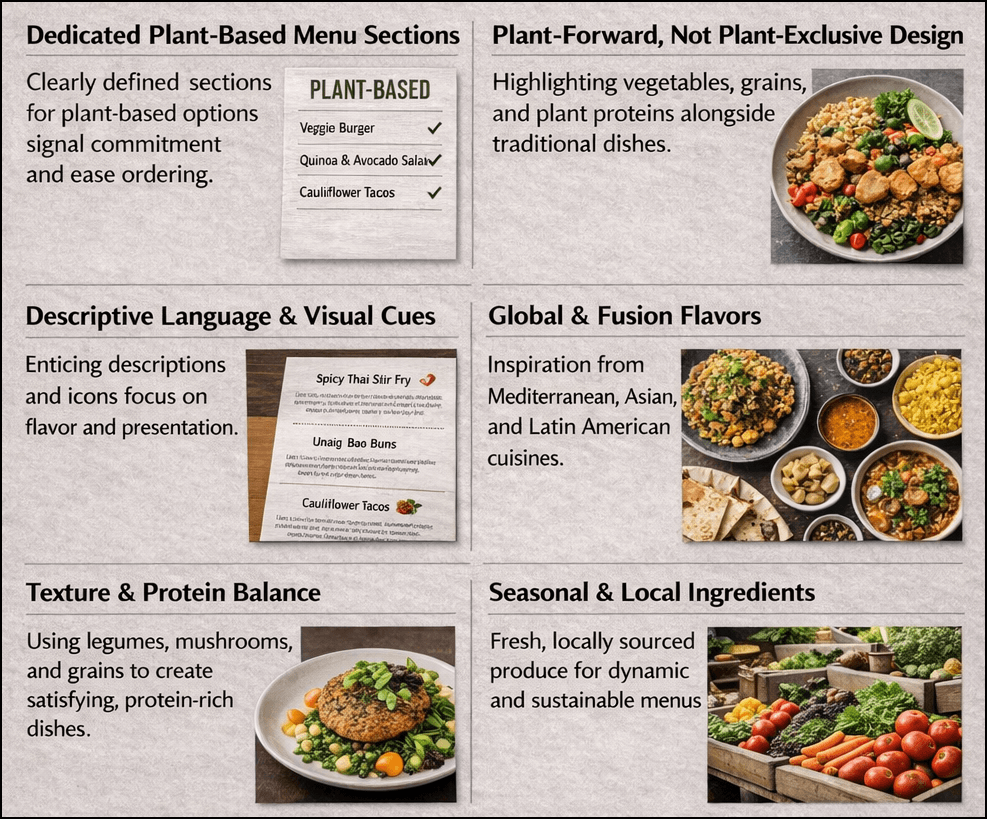
By designing plant-based meals with the same creativity and culinary rigor as traditional dishes, restaurants avoid positioning them as compromises and instead elevate them as premium offerings.
Check out Tech Transforming the Restaurant Dining Experience, which explores how digital tools, smart systems, and emerging technologies are enhancing customer experience, streamlining operations, and reshaping modern dining.
Operational and Kitchen Adaptations Supporting Plant-Based Meals
Adapting to plant-based demand requires more than menu updates—it also involves changes in kitchen workflows, equipment usage, and staff training.
-
Dedicated Prep Areas to Prevent Cross-Contamination: Restaurants increasingly implement designated preparation zones for plant-based ingredients to avoid cross-contact with animal products. This is essential for meeting dietary expectations and building customer trust.
-
Revised Cooking Techniques and Equipment Usage: Plant-based cooking often emphasizes roasting, fermentation, steaming, and slow cooking rather than high-fat grilling or frying. Kitchens adapt by optimizing ovens, steamers, and prep equipment for vegetable-forward production.
-
Ingredient Storage and Inventory Management: Plant-based menus rely heavily on fresh produce, grains, and specialty ingredients that require different storage conditions than meat. Restaurants adjust refrigeration layouts and inventory rotation practices to minimize waste and maintain freshness.
-
Staff Training and Culinary Education: Kitchen teams receive training in plant-based cooking techniques, flavor development, and nutritional balance. Front-of-house staff are also trained to confidently explain ingredients, preparation methods, and dietary suitability.
-
Streamlined Production for High-Volume Service: In 2026, plant-based meals will no longer be low-volume orders. Restaurants design scalable recipes and batch-prep strategies to ensure consistency during peak service periods without compromising quality.
These operational changes help integrate plant-based meals seamlessly into daily restaurant workflows rather than treating them as exceptions.
Explore Contactless Dining Technology: Reshaping the Future of the Restaurant Industry, which explains how touchless ordering, digital payments, and smart service solutions are transforming restaurant operations and customer experiences.
Sustainability, Cost Control, and Supply Chain Advantages
Beyond consumer appeal, plant-based meals offer restaurants measurable operational and financial benefits.
-
Lower Ingredient Cost Volatility: Plant-based ingredients often experience less price fluctuation than meat and seafood, helping restaurants stabilize food costs and plan menus more accurately.
-
Reduced Waste and Spoilage: Vegetables, grains, and legumes can often be repurposed across multiple dishes, reducing trim waste. Creative use of stems, peels, and surplus produce further supports waste reduction goals.
-
Improved Energy and Resource Efficiency: Plant-based cooking generally requires less energy-intensive storage and preparation than animal proteins. Reduced reliance on freezing and high-temperature cooking lowers utility consumption.
-
Alignment with Sustainability Certifications and Regulations: Many regions in 2026 incentivize sustainable practices through certifications, grants, or regulatory preferences. Plant-based menu adoption helps restaurants meet environmental benchmarks and reporting requirements.
-
Brand Differentiation and Long-Term Loyalty: Restaurants that commit to sustainability and plant-based innovation strengthen brand identity, attracting ethically minded consumers and enhancing long-term loyalty.
-
Key Restaurant Segments Leading Plant-Based Adoption: Plant-based dining is expanding across multiple restaurant formats, each using plant-forward menus to meet demand and improve efficiency.
The table below outlines how different segments adopt plant-based meals and the benefits they gain.
|
Restaurant Segment |
How Plant-Based Meals Are Used |
Business & Operational Benefits |
|
Fast-Casual & Quick-Service Restaurants |
Plant-based bowls, wraps, and customizable meal options |
High service speed, menu flexibility, and strong demand from health-focused customers |
|
Casual Dining Restaurants |
Plant-based entrées are integrated alongside traditional menu items |
Menu inclusivity for mixed-diet groups, increased customer satisfaction, and repeat visits |
|
Fine Dining & Chef-Driven Concepts |
Seasonal, chef-curated plant-based dishes showcased as signature offerings |
Brand differentiation, premium positioning, enhanced sustainability storytelling |
|
Corporate, Institutional & Healthcare Food Service |
Wellness-oriented plant-based meals supporting dietary diversity |
Nutritional compliance, scalability, alignment with health and sustainability initiatives |
|
Ghost Kitchens & Delivery-Only Brands |
Delivery-optimized plant-based concepts with simplified customization |
Lower ingredient risk, efficient operations, and high appeal to younger urban audiences |
These segments show that plant-based dining is now a scalable, profitable strategy, driving menu innovation and long-term growth across the restaurant industry.
Summary: The Future of Plant-Based Dining in the Restaurant Industry
In 2026, plant-based meals are no longer optional—they are strategic menu elements that support consumer demand, operational efficiency, and sustainability goals. Restaurants that treat plant-based dining as a core culinary focus, rather than a trend, gain long-term relevance in a competitive market. By redesigning menus, adapting kitchen operations, and aligning with sustainability values, operators benefit from greater flexibility, cost stability, and stronger brand differentiation as plant-based dining continues to shape the future of foodservice.
Key Takeaways
-
Plant-based meals have become mainstream dining expectations in 2026
-
The menu redesign emphasizes flavor, texture, and global culinary inspiration
-
Kitchen operations adapt to new ingredients, prep methods, and workflows
-
Sustainability and cost control drive long-term adoption
-
Multiple restaurant segments are leading plant-based innovation
Looking for dependable restaurant equipment parts online in Canada? Shop now at PartsFe CA, we provide high-quality replacement parts for a wide range of restaurant equipment, including ovens, fryers, refrigerators, ice machines, and food prep appliances. Sourcing from trusted commercial brands, we combine competitive pricing, fast shipping, and responsive customer support to help foodservice operators reduce downtime, maintain peak performance, and keep kitchens running efficiently.
Reference:
https://www.fao.org/home/en/
https://www.usda.gov/food-and-nutrition/food-systems/plant-based-diets
FAQs
Do plant-based menus reduce operating costs for restaurants?
Yes. Plant-based ingredients often have more stable pricing, lower spoilage risk, and support efficient prep methods, helping restaurants control food and energy costs.
Are plant-based meals only for vegan customers?
No. Most plant-based menu items in 2026 are designed for all diners, offering flavorful, satisfying options that appeal to mixed-diet groups.
Will plant-based dining continue to grow beyond 2026?
All indicators suggest continued growth, driven by innovation, sustainability initiatives, and evolving consumer expectations across global food service markets.